When planning for disaster, we run through scenarios in our mind and those scenarios give us a visual baseline for which we make plans. As preppers we talk a lot about the steps you can take right now to get prepared so that you will have a plan, supplies and options for when that disaster may strike. Often preparedness deals with the immediate effects of disaster like having a vehicle to bug out or having plenty of food and water to deal with shortages. The next logical step from that is a longer term plan, but those long term prepping plans usually revolve around extensions of those same basic needs: Food, Water, Shelter and Security.
Take any crisis with a timeline much longer than we associate with “typical” natural disasters and you need to consider different items as part of your planning. For a “typical” emergency, the chaos is relatively short lived. Even though the rebuilding and recovery process may take years, the process can start as soon as the dust has settled, the earth has stopped shaking, and wind no longer howls, the fires are extinguished, the rains have stopped or the water has receded. We shed tears and hopefully hug all of our loved ones and start to pick up the pieces.
But what about a scenario that just doesn’t stop? What if you are visited by the potential threats of a new fresh hell every day? We hopefully plan for food that we can eat off of and grow for future needs. We can band together with others in our neighborhood for security or devise alternative energy schemes to keep the lights on. We rarely talk about the stress, anguish and for some, crippling fear that could be a part of life in the worst apocalyptic view of the future. You have plans for everything else, but do you have a plan for coping with stress after disaster?
First world problems
It’s interesting to try and research stress from the standpoint of some end of the world as we know it perspective. So much of our current world is about as far away from disaster as you can be. In the U.S. currently, we lead very comfortable lives when compared with large parts of the rest of the world. Don’t get me wrong, I am not apologizing for that at all, but it does change how you view stress.
We have a running joke in my family and I am sure we aren’t alone in this of whenever one of us encounters something that irritates us or “stresses us out” we jokingly, but accurately label that as a “first world problem.” If I can’t find any good movies out of the thousands available to me via the internet piped into my living room, that is a first world problem. If my computer is not running as fast as I want as I sit in an air-conditioned home or I have to wait 3 minutes for it to reboot due to a free OS upgrade, that is a first world problem. If I have to leave the security of my bathroom to walk two feet to a closet with dozens of rolls of soft toilet paper… you get the point. We don’t have anywhere near the stress in our lives now that some people do and we frequently take that for granted. I don’t expect anyone to sit and feel ashamed for our lifestyle, but what will you do if that is all gone?
Imagine the father who has walked hundreds of miles with his family across a desert to avoid ethnic cleansing or the mother who is alone with three small children living in a refugee camp. The same camp with hundreds of thousands of other displaced people where she is lucky to have a small meal of watery rice a couple times a day. Oh, did I mention that she has to walk almost a mile to stand in line for that rice and she goes back to a tent to live in with 15 other families. I won’t even mention the people who are still running for their lives from groups bent on their complete destruction who kill men, women and children with machetes. We don’t know real stress in the US right now.
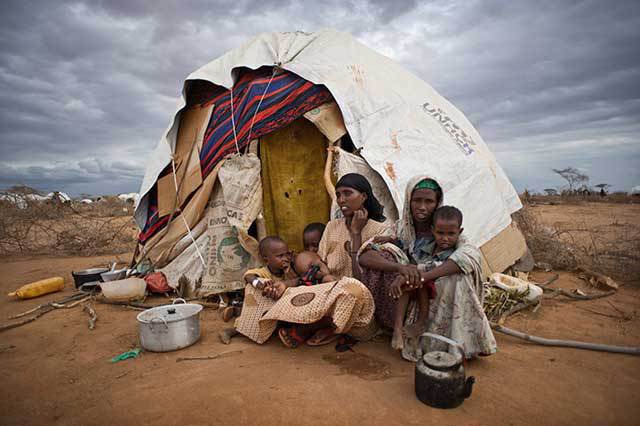

You can find lots of information about the “stress” we do have in our lives and plenty of advice for dealing with stress. In a disaster, getting fresh air or exercise probably won’t cut it but that does say something about what we do all day. I think in a crisis like many of us are expecting in our worst nightmares, our very definition of stress will be radically rewritten. Even if nothing that bad happens, stress and I mean real stress is something we should plan for.
What are some symptoms of stress?
- Frequent headaches, jaw clenching or pain
- Gritting, grinding teeth
- Stuttering or stammering
- Tremors, trembling of lips, hands
- Neck ache, back pain, muscle spasms
- Mood-swings and easy bouts of crying.
- Overwhelming guilt and self-doubt.
- Difficulty sleeping.
- Low threshold of frustration.
As preppers reading this article I have to assume that you will be leaders to the people in your group. Recognizing stress will be important for a couple of reasons. First you want to be able to identify situations where someone needs a little extra care, assistance or rest. Stressed out individuals can make mistakes that could get people hurt or killed. I am not talking about the kind of stress caused by not having enough space on your smart phone to take a one hour video of your daughter’s birthday party at Chuck-E-Cheese either.
When you are living with loss, possibly death, great uncertainty or dangers to your safety, people can deal with stress in a number of ways. I think at some point stress will become a part of life and you will have peaks and valleys depending on the relative safety and security you are living in at any moment but when your entire life has been thrown into a blender and dumped on the ground, stress might take it’s toll for a while.
How can you deal with stress?
Each person deals with stress in their own way and in a disaster it would be perfectly normal to have feelings of sadness or loss and uncertainty. You as a leader will be living with stress just like anyone you come in contact with most likely and if you know how to deal with your own stress you will be better prepared to help others like a spouse, children or parent deal with their own stress.
Stress frequently brings dark feelings and doubt to the surface. It is very normal to want to lash out when you are stressed, to hit back at the situation that has impacted your life. Sometimes this may work to your benefit, but for most times I think you want to reserve anger like that. What can you do?
Focus on what you can control – We can easily dwell on the problems we can’t fix right now and worry about how that will change. There are so many things to consider when we are in a stressful environment and that is one additional reason to prepare now so that all of the basics of life and security will be checked off the list.
Admit you are stressed out and talk about that with someone – When I am stressed, I tend to focus on all of the things I am worried about. I rush through my day trying to knock things off my list or thinking about them until I reach some level of satisfaction about where I am. I don’t normally go to my wife to discuss things I am stressed out about but she seems to know when I am stressed and engages me to talk about it. Even though the things I am worried about don’t disappear, it helps to talk. Sometimes she does help me with ideas or just a different perspective. I would never want to be without her counsel.
Don’t blame yourself for bad things – I know that personally, I prepare because in the back of my mind I feel responsible for my family and I don’t want to let them down in an emergency. Its one thing if Dad forgets to stop at the store and get ice cream for dessert (first world problem) but another thing entirely if a storm knocks out power for two weeks and I can’t keep them warm and fed. There will be things you can’t control and dwelling on what you should have done is useless. Focus on what you can do, make things happen and move on.
Sleep, eat and drink – Our bodies are amazing creations and so many problems can be remedied themselves with the simple basics our bodies need to function properly. Making sure you get enough sleep is an important stress reducer. You also need to make sure that applies to everyone in your group. That is another reason why a group of people is better than lower numbers of people so that you have more people to work, stand guard and help. Food and Water is the fuel our bodies need to function at peak capacity. So that should be one of the first things you check off on your prepper to do list. See a theme here?
Rely on your higher power – The saying goes that there are no atheists in foxholes and that simply means that when you are worried about dying, you start to believe/hope for an afterlife and a loving God to watch over you and keep you safe. Many of us already have a spiritual component in our lives and we should be embracing this daily. You can certainly lean heavily on your own higher power for strength and peace in a time of high stress. Sometimes a simple prayer is all it takes to calm me down and I know that if I ever was in a real “stress” inducing situation I would be praying much more often than I do now.
How do children react to stress?
Adults are one thing and you might think we can do what they did in old movies. Just slap the person going hysterical and yell at them to “Snap out of it”! That may work, actually it might feel pretty good depending on the person on the receiving end of the slapping. Just kidding… sort of.
Children are different though so understanding the stress from their eyes will help you deal with them in ways that make them feel better. Children all deal with stress differently at different ages. This is a breakdown from FEMA:
Birth through 2 years. When children are pre-verbal and experience a trauma, they do not have the words to describe the event or their feelings. However, they can retain memories of particular sights, sounds, or smells. Infants may react to trauma by being irritable, crying more than usual, or wanting to be held and cuddled. The biggest influence on children of this age is how their parents cope. As children get older, their play may involve acting out elements of the traumatic event that occurred several years in the past and was seemingly forgotten.
Preschool – 3 through 6 years. Preschool children often feel helpless and powerless in the face of an overwhelming event. Because of their age and small size, they lack the ability to protect themselves or others. As a result, they feel intense fear and insecurity about being separated from caregivers. Preschoolers cannot grasp the concept of permanent loss. They can see consequences as being reversible or permanent. In the weeks following a traumatic event, preschoolers’ play activities may reenact the incident or the disaster over and over again.
School age – 7 through 10 years. The school-age child has the ability to understand the permanence of loss. Some children become intensely preoccupied with the details of a traumatic event and want to talk about it continually. This preoccupation can interfere with the child’s concentration at school and academic performance may decline. At school, children may hear inaccurate information from peers. They may display a wide range of reactions — sadness, generalized fear, or specific fears of the disaster happening again, guilt over action or inaction during the disaster, anger that the event was not prevented, or fantasies of playing rescuer.
Pre-adolescence to adolescence – 11 through 18 years. As children grow older, they develop a more sophisticated understanding of the disaster event. Their responses are more similar to adults. Teenagers may become involved in dangerous, risk-taking behaviors, such as reckless driving, or alcohol or drug use. Others can become fearful of leaving home and avoid previous levels of activities. Much of adolescence is focused on moving out into the world. After a trauma, the view of the world can seem more dangerous and unsafe. A teenager may feel overwhelmed by intense emotions and yet feel unable to discuss them with others.
Coping with stress may not be the first thing we consider when we are prepping, but it is a natural by-product of the events we are planning for. Your job as leader won’t end simply at gathering supplies. You will also have to provide strength and compassion and understanding as appropriate to help others around you. I don’t expect to turn into a touchy feeling – hug it out kind of guy when we are trying to survive and cannibals are munching on your legs. That is just not in my nature and I will be focusing on other things I assume. I do think it’s important to be able to realize how each person is dealing with the stresses in their lives. You can use this to help people by guiding them in certain directions or collaborating with others to provide assistance while you focus on slaying the metaphorical dragon.
Call it prepping for the emotional component of your group under duress. It is something that we all should spend a little time thinking about. You could be the person who brings someone through their stress and helps them survive. Helping others cope might even help you in the end.