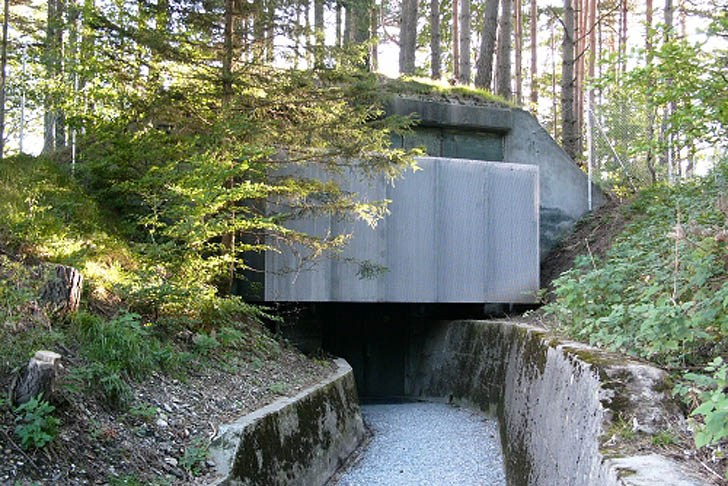
I want to talk about what I believe to be the most critical necessity in the event the SHTF: The ability to shelter in place, in a shelter that provides protection from radiation, bombs, attacks, tornadoes and numerous other threats to safety.
While there are above ground shelters that do offer protection from some of the above mentioned threats, hands down, the best place to be is UNDERGROUND.
That said, with the exception of a line of Tornadoes passing through, you need to be psychologically and physically prepared to go underground for at least 2-3 weeks.
The amount of time will of course depend on the extent and type of event that has or is occurring.
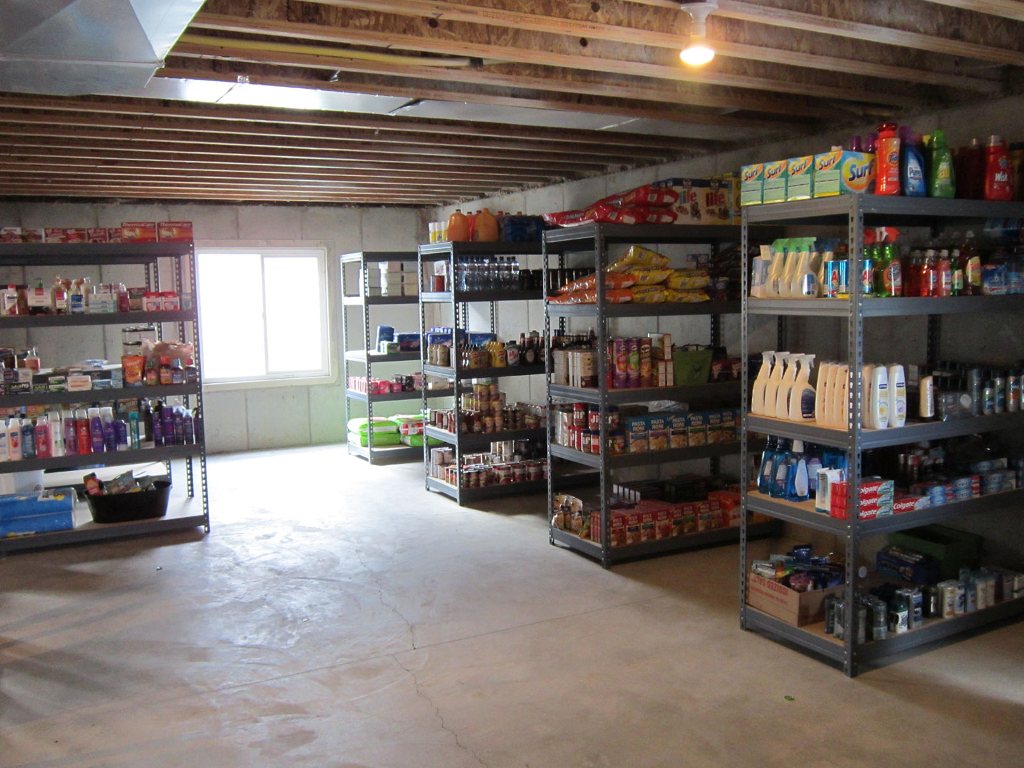
Let’s assume you have a bunker and did your homework and have an adequate supply of MRE’s, water and other necessities for what could be your INITIAL 2-3 week stay.
What is the best bunker design?
I want to address the psychological aspect of being underground, in a confined space, and the issues/considerations faced by the occupants with regard to the Type, Shape and Utility of your surroundings.
Let’s face it, practical and usable space quickly becomes a valuable commodity when you are going to spend a significant amount of time in the shelter before venturing topside, and that environment should be comfortable, healthy and space efficient. You are going to be stressed enough if you are in there, and the last thing you need is the additional stress of a cramped, unfriendly environment.
I present this question for your consideration: Would you rather be in a claustrophobic steel pipe or in the open area provided by a square-shaped reinforced concrete bunker that is already finished with non-toxic material?
If steel pipes and steel boxes were the best shelter platform, the Military would be using them, and they’re not….they are still using reinforced concrete. There has to be something to be said about that, and there is: Mass, Density, Thermal Resistance, Sound Attenuation and Cost, to name a few.
Furthermore, steel shelters, which are typically 3/16- 1/4 of an inch thick, need to be buried DEEP, in order to provide the proper comparative level of protection against radiation. They are typically installed with 8-10 feet of earth covering the top and this presents a considerable number of challenges with regard to the costs for excavating, the need to hire a crane and other issues.
For example, a 10 foot Pipe that is 20 feet long will require an 18-20 feet deep hole and provides a gross interior area of 1,570 cubic feet. Keep in mind that the interior surface is curved ( similar to being in a submarine ), and therefore requires a floor to be installed, which reduces headroom. Simply put, a pipe doesn’t lend itself to being space efficient and comfortable.
Comparatively, a 10 foot tall, 10 foot wide and 20 foot long Concrete shelter will only require a 12-13 foot deep hole, provides a gross interior area of 2,000 cubic feet, does not require a floor to be installed, has no loss of headroom anywhere inside the structure and only needs to have 2-3 feet of earth cover overhead.
If the height of the Concrete shelter is decreased to 8 feet ( the same height of the ceilings in your home), the required depth of the hole is reduced to 10-11 feet and the gross interior area is 1,600 cubic feet. This is still more than a 10 foot pipe of the same length while also providing complete use of the space, as the side walls are not coming in toward the center as they do in a pipe.

In my opinion, the 2 feet of headroom throughout is more than adequate.
Having adequately addressed the space issue, I’d like to make a quick point on the use of ICF’s (Insulated Concrete Forms) for long-term underground shelters.
ICF’s are made of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) foam blocks that are put together like Leggo’s, a double row of rebar is installed as the foam blocks are connected and when the walls are completed, concrete is pumped into them.
Of biggest concern with these systems is the fact that the Polystyrene contains toxic chemicals. Not only because they are made of petroleum-based foamed plastics, but also because they contain fire-retardant chemicals that are also toxic. Among these chemicals is HBCD (Hexabromocyclododecane).
HBCD has been classified as a category 2 for reproductive toxicity.[6] Since August 2010 Hexabromocyclododecanes are included in the EPA‘s List of Chemicals of Concern.[7] On May 2013 the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) decided to include HBCD in the Convention’s Annex A for elimination, with specific exemptions for expanded and extruded polystyrene in buildings needed to give countries time to phase-in safer substitutes. HBCD is listed for elimination, but with a specific exemption for expanded polystyrene (EPS) and extruded polystyrene (XPS) in buildings.
Additionally, EPS is labeled a flammable material and MUST be covered with a non-flammable material such as fire rated sheetrock or masonry to limit surface exposure to possible ignition sources. This covering also reduces exposure to the off-gassing of other chemicals considered to be toxic that occurs without exposure to fire.
When it burns, EPS produces heavy, acrid and toxic smoke. This obviously presents another serious problem when you are in a confined space, from which there is no escape. Even a small event in which this material merely smoldered with no open flame can/would have dire consequences for the occupants. Exposure to the heavy smoke generated, even if only for a few minutes, has been shown to be lethal.
In short, you are looking for your shelter to provide you a safe, healthy and fireproof refuge from a multitude of disaster scenarios. The dangerous and potentially lethal points made above should not be overlooked when making a decision in choosing a bunker or shelter.